Research Article - Clinical Schizophrenia & Related Psychoses ( 2023) Volume 17, Issue 4
Mental Health Policies and Regulations Impacting Psychiatric Nursing Practice in Saudi Arabia
Wael Habib Alanazi1, Abdulrahman Nayir Alanazi1, Faisal Najem Khalaf Aljohani1, Sehrish Khan2*, Nazzal Mayoof Sair Alenezi1, Meshari Hussain Alanazi1, Mohammed Awad Alanazi1, Fahad Awadh Dughayman Alanazi1, Abdulkarim Sagi Alenezi1 and Nawaf Mohammed Al Dahou Al Hazmi12Department of Psychology, Institute of Clinical Psychology University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan
Sehrish Khan, Department of Psychology, Institute of Clinical Psychology University of Karachi, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan, Email: amiu.research@gmail.com
Received: 06-Oct-2023, Manuscript No. CSRP-23-116032; Editor assigned: 09-Oct-2023, Pre QC No. CSRP-23-116032 (PQ); Reviewed: 23-Oct-2023, QC No. CSRP-23-116032 (QC); Revised: 30-Oct-2023, Manuscript No. CSRP-23-116032 (R); Published: 06-Nov-2023, DOI: 10.3371/CSRP.AWAA.100623
Abstract
Background: Mental health policies and regulations are essential within the psychiatric setting as they help and show the direction to provide adequate service to the patients. It is also crucial that a psychiatric institute regulate the mental health of psychiatric nurses as they constantly work with psychiatric patients, which makes them overwhelmed. This article examines the mental health policies and regulations affecting psychiatric nursing practice in Saudi Arabia.
Method: To classify necessary research published between 2019 and 2023, a comprehensive search of databases, including Scopus, PubMed and Web of Science, was done. The inclusion criteria for this study were studies written in English that specifically studied the impact and results of mental health policies and regulations affect psychiatric nursing practices. Furthermore, the studies chosen had to use well-established scales for measurement and provide valuable data on team dynamics. Ten studies were included in the synthesis after initial screening and quality assessment.
Results: The result identified the six themes, which are educational interventions to increase the practice of psychiatric nursing; mental health challenges affect psychiatric nurses' practices; institutional policy impact on psychiatric nurses' practices; mental health regulation and stigmatization; developing professional attitude toward psychiatric disorder and defined psychiatric nurse’s roles within the psychiatric setting enhance psychiatric practice.
Conclusion: It is concluded that defined roles, psychiatric institutions’ rules and regulations, and education and training provided to the psychiatric nurses have positively related to nurses' practice within the psychiatric ward. The more policies are defined for psychiatric nurses, the more effective service or treatment they provide to the patients.
Keywords
Mental health • Policy • Regulation • Psychiatric nursing • Practice • Mental health challenges • Databases
Introduction
Mental health is a crucial human right that enables individuals to cope with life’s stresses, realize their skills, learn, work and contribute to their municipalities. It is a complex continuum, varying in severity and outcomes. Mental health conditions include mental disorders, psychosocial disabilities and other mental states associated with distress or self-harm risk. While some may experience lower mental well-being, this is not always true [1,2].
With increased attention on the international health agenda, mental health is a significant worldwide public health concern. Nevertheless, there is a requirement for a distinct evaluation of international mental health funding. According to an assessment of global development support for people's mental wellness between 2006 and 2016, less than 0.5% of the entire health development funding was dedicated to mental health. International organizations and development partners are criticized for their repeated efforts to raise financial support for mental health, given the poor and middle-income nations' where there is limited public investment in this field [3].
Promoting, preventing, treating, rehabilitating, caring for, and recovering are the main objectives of the multi-sector action plan for mental health. It was created after discussions with member states, civil society organizations and foreign partners. The program suggests important metrics and targets to assess implementation, progress and effect and lays out specific activities for member states, the secretariat and international partners. Individuals with good mental health can deal with life's difficulties, work productively and give back to their communities. The plan also highlights how children develop a strong sense of self control over their thoughts and emotions, form relationships with others, and obtain the necessary education to take an active societal role [4,5].
Qatar National Vision is a national policy framework for drug usage and mental health in Qatar. To create its mental health services and pertinent policies, Qatar, a quickly rising, high-income nation with a population of more than 2.5 million, has incorporated international best practices. Arabic and Islam are the official languages, and the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita ranks among the highest in the world. Foreigners comprise over 75% of the population, with lower-skilled migrants making up half [6].
For efforts to change policy and practice, it is essential to comprehend the patient experiences of incarceration under mental health laws. Even though involuntary inpatient treatment is frequently unpleasant and distressing, several elements have been found to help to mitigate these adverse effects. Inpatient wards may benefit from developing new working practices that give patients and staff more voice and create social and physical settings that support recovery [7].
Following the Mental Health Services Act (MHSA) passage and throughout the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, there was an increase in public interest in mental health. Definitions, translations, factors, services, policies, unpleasant mental states and their context during the pandemic were among the top and rising linked questions. Legislative changes could be used to address any possibilities or impediments presented by policies at the national, state and local levels. Although localities have different processes for passing bills, ordinances and other forms of legislation, elected representative bodies usually must approve new laws before the head of the executive branch signs them into law. There are several different types of legislation, such as those that demand reporting and oversight procedures, authorize the creation of new agencies and programs, and reorganize those that already exist [8-10].
Public response and service modifications address mental health difficulties, emphasizing infection control, diagnosis, and treatment accessibility, continuity of care, and attention to new cases and high-risk populations. To reduce gaps in healthcare provision, specialists, physicians and service consumers should design sustainable delivery systems for mental healthcare among psychiatric nurses [11].
Each of the study's bad mental health outcomes had higher scores when interpersonal relationships, organizational support, organizational readiness, safety in the workplace and accessibility to supplies and resources were negatively rated. Given their alarming self-reports of their mental health during the COVID-19 epidemic, better workplace regulations and procedures are urgently needed to avoid and alleviate nurse’s unfavourable working conditions [12].
Nurses are among those in the medical field most at risk of contracting COVID-19 and dying from it because of the conditions in the workplace, such as a lack of personal protective equipment, a lack of staff, and insufficient safety training and planning. According to preliminary studies, nurses are a group that is particularly vulnerable to the COVID-19 pandemic’s adverse effects on mental health. The lack of mental health issues such as Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), anxiety, depression and burnout is frequently used as a proxy for mental health in nursing research. Hypervigilance, poor focus, workplace avoidance, nightmares and flashbacks to the traumatic event are all symptoms of PTSD, which can appear after a traumatic experience [13-17].
The physical, emotional and psychological health of healthcare workers is seriously in danger due to the rising prevalence of violence, especially among psychiatric nurses. Despite acknowledging that this behaviour is part of their job, female nurses said institutional supervisors, peers and relatives didn't offer much encouragement [18].
Mental health nurses often grapple with paternalism and ethical concerns, making it crucial to address this moral dilemma. This review can help healthcare professionals understand their ethical obligations to people with mental illnesses, including preventing discrimination, defending human rights, respecting autonomy and ensuring individual independence. Nurses can conduct themselves ethically by discussing potential solutions, benefiting the profession, patients and the public [19-21].
Materials and Methods
Research objective
The present systematic review proposes scrutinizing the mental health policies and regulations impacting psychiatric nursing practice in Saudi Arabia.
Research questions
In this systematic review, the research questions include the following;
• What are the mental policies and regulations for Saudi Arabia's psychiatric nurses?
• How do mental health policies and regulations impact psychiatric nursing practices in Saudi Arabia?
Literature search strategy
A detailed and methodical examination of academic databases identified relevant papers published in peer-reviewed journals. PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science were among the searchable databases to be searched. The search phrases were chosen with care to include relevant themes, such as “Mental health policies”, “Mental health regulation”, “Mental health policies and regulation”, “Mental health policies and regulation impact”, “Psychiatric nursing”, “Mental health policies and regulation impacting psychiatric nursing in Saudi Arabia”. This search strategy was clearly explained in Tables 1 and 2.
| Syntax | Policies |
|---|---|
| Syntax 1 | "Mental health policies", "Nursing", "KSA" |
| Syntax 2 | "Mental health regulation", "Nursing", "KSA" |
| Syntax 3 | "Mental health policies", "Impacting", "Psychiatric nursing", "KSA" |
| Syntax 4 | “Mental health regulation", "Impacting", "Psychiatric nursing", "KSA" |
| S. no. | Database | Syntax | Year | Number of researches |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PubMed | Syntax 1 | 2019-2023 | 4 |
| Syntax 2 | 18 | |||
| Syntax 3 | 3 | |||
| Syntax 4 | 0 | |||
| 2 | Scopus | Syntax 1 | 678 | |
| Syntax 2 | 687 | |||
| Syntax 3 | 470 | |||
| Syntax 4 | 80 | |||
| 3 | Web of Science | Syntax 1 | 154 | |
| Syntax 2 | 128 | |||
| Syntax 3 | 95 | |||
| Syntax 4 | 74 |
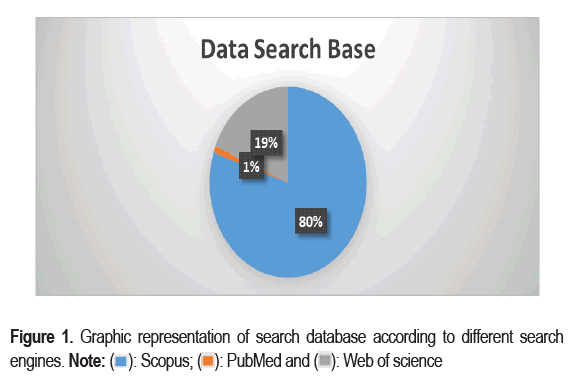
To discover relevant research publications, three prominent databases were used: Scopus, PubMed and Web of Science. The search was chosen to assure validity and applicability focused on papers issued during 2019 and 2023. According to the statistics, Scopus produced the most significant research articles, totalling 1915. PubMed contributed 25 pieces of research, while Web of Science contributed 451. These findings show the thoroughness of the scientific search and lay a solid foundation for the next steps of the systemic review as shown in Figure 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The study requires English-language communication, full-text papers published between 2019 and 2023, and research on mental health policies and regulations impacting psychiatric nursing practice in Saudi Arabia. Exclusions include non-English, older than 2019 and grey articles.
Study selection
Data search includes identifying, monitoring, maintaining, formulating and synthesizing concepts. It begins with study selection and search engine identification using inclusion and exclusion criteria. Databases, search engines, and literature libraries are used as shown in Table 3 [22-30].
| S. No. | Author | Research | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alzahrani et al. [22] | Effectiveness of an educational intervention on clinical competency among mental health nurses working at a government mental health hospital | 2023 |
| 2 | Aljohani et al. [23] | Community mental health nursing in Saudi Arabia: Current and future challenges | 2021 |
| 3 | Alyousef et al. [24] | Nurse views of obstacles nurses encounter in Saudi Arabia while providing psychiatric care | 2023 |
| 4 | Alzghool et al. [25] | The future of mental health nursing practice in Saudi Arabia | 2019 |
| 5 | Alhawsawi et al. [26] | Nurses’ attitude towards patient’s rights at Erada mental health complex in Jeddah city, Saudi Arabia | 2022 |
| 6 | Aldhafeeri et al. [27] | Difficulties experienced by psychiatric nursing in mental health hospitals and clinics and their relationship to performance improvement | 2022 |
| 7 | Aljohani et al. [23] | Community mental health nursing in Saudi Arabia: Current and future challenges | 2021 |
| 8 | Alyousef et al. [28] | Evaluating the need for supervision of advanced mental health practitioners in psychiatric practices in Saudi Arabia | 2022 |
| 9 | Alhamidi et al. [29] | Perceptions of Saudi psychiatric mental health nurses’ roles in the inpatient mental health care setting | 2023 |
| 10 | Alotaibi et al. [30] | Assessing perceptions about critical thinking, motivation learning strategies in online psychiatric and mental health nursing education among Egyptian and Saudi undergraduate nursing students | 2023 |
Results
Identification of studies via databases and registers
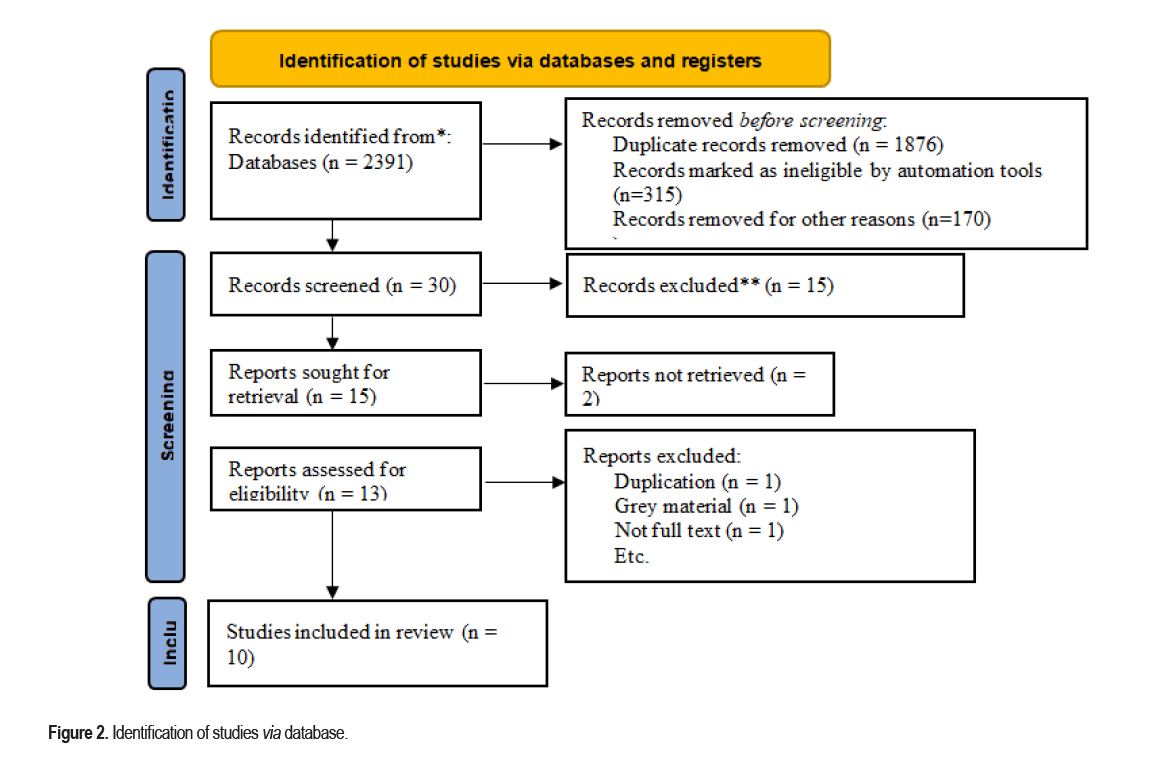
A study’s quality can be systematically evaluated using data from peer-reviewed journals, overall assessment and quality management. This process is known as quality evaluation. This comprehensive review of the literature contains a great deal of information on research technique and the study to apply pressure as shown in Figure 2.
Data extraction
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), a technique to examine the impact of mental health policies and regulations on psychiatric nursing practice in Saudi Arabia, was used to extract the data. The criteria for inclusion and exclusion were study parameters, participant characteristics and measurements as shown in Table 4 [22-29].
| Author | Aim of study | Methodology | Sample | Setting | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzahrani et al. [22] | To evaluate the effectiveness of an educational intervention on the clinical competency of mental health nurses | Quasi-experiment study pre-test and post-test with one group study design were conducted | 80 nurses in a large mental health hospital | Tabuk city, Saudi Arabia | The collected data analysis revealed a statistically significant positive effect of educational programs on improving mental health clinical competency, hence, healthcare organizations and senior decision-makers should develop well designed periodic mental health programs that involve nurses who have a master's and doctorate degrees in mental health nursing to enhance mental health clinical competency |
| Alotaibi et al. [30] | Examines student perceptions about critical thinking, motivation and learning strategies in online psychiatric nursing education among nursing students | Quantitative research design | A total of 75 Saudi undergraduates and 105 Egyptian nursing students | At Imam Abdulrahman bin Faisal University in Saudi Arabia and Alexandria University in Egypt | The current study found that using a motivating method for online learning inspired students to engage in critical thinking and cognitive processing strategies in a psychiatric and mental health nursing course, even in two different contexts |
| Aljohani et al. [23] | Aimed to explore the current and future challenges that facing the application of community mental health nursing | A Delphi method was used in this research. The data was collected over three rounds. For the first round the researcher utilized three open-ended questionnaires. | 29 participants | In Saudi Arabia | The results of the study showed that consensus among the experts were reached on 18 elements with agreement level of 70% or more. 5 of them on the current challenges, 3 on the potential future challenges and 10 on the suggested methods on how to start implementing the community mental health nursing |
| Alyousef et al. [24] | Study offers a description of mental health nurses viewpoints, insights into obstacles encountered during their experiences and recommendations for enhancing psychiatricinpatientnursing careand achieving progress toward the goals set out by KSA vision 2030 | A phenomenological qualitative design | 10 mental health nurses | In KSA | Two main themes and related subthemes were identified. The first theme-obstacles faced by mental health nurses were composed of the following subthemes: Policy at institutions; clear job roles; low professional self-confidence and inadequate support; stressed, insecure and unsafe, and stigmatization. The second theme-recommendations to improve the quality of mental health nursing were composed of two subthemes: To enhance mental health awareness and improve professional skills and education |
| Alzghool et al. [25] | The aim of this study was to explore the future directions of mental health nursing practice in Saudi Arabia by obtaining expert consensus and to recommend a future agenda for policymakers and researchers in the field of mental health nursing. | A Delphi method was used. The data was collected over three rounds. For the first round, the researcher utilized open-ended question questionnaire. Following the content analysis of the open-ended questions (639), responses was elicited | The content analysis of the open-ended questions (639) responses was elicited | In KSA | The results of the study showed that consensus among the experts were reached on 19 elements with agreement level of 80% or more. In conclusion, it was apparent that expert panel believes that there are many elements that should shape up the future of mental health nursing practice by 2025. However, less emphasis was apparent from the panel ratings on items such as the stigma associated with mental illness and mentally ill people |
| Alhawsawi et al. [26] | The purpose of the study is to investigate the attitudes of psychiatric nurses at Erada mental health complex in Jeddah city towards patient’s rights | A descriptive cross-sectional research design | The study used the convenient sampling method to recruit a sample of 171 psychiatric nurses | In KSA | The results of the study showed that psychiatric nurses at Erada mental health complex had positive attitudes towards patients’ rights (4.06 ± 0.76). The results showed that the highest positive attitudes were related to those patients should receive healthcare services in safe environment, having the right to choose the healthcare providing institution or change it if needed, and the right to benefit from any provided healthcare services that comply with their medical condition. In addition, it was found that there were no significant statistical differences in the psychiatric nurses’ attitudes towards patients’ rights referred to nurses’ age, gender, or years of experience. |
| Aldhafeeri et al. [27] | This research explored difficulties experienced by psychiatric nursing in mental health hospitals and clinics and their relationship to performance improvement | The study followed the correlation and the descriptive design | 201 participants (nurses) from a Mental Health Hospital in Hafar Al-Batin, King Khaled General Hospital clinic, and Hafar Albaten Central Hospital clinic-Saudi Arabia | In Saudi Arabia-Hafar Al-Baten | Results showed that 56% were males while 44% were females. The large percentage according to age was 47.8% to the range age group from 20-29. Then the age group from 30-39 with total number 42 and percentage 20.2%. Regarding study sample years of experience, the high percentage was from 5 years-7 years with 57%. Also, showed that nurses faced many difficulties such as depression, stress and anxiety during their work shift. These symptoms can adversely affect work performance and care quality. No statistically significant relationship between the overall degree of the mental health scale and the professional performance scale |
| Aljohani et al. [23] | The aim of this study was to explore the future directions of mental health nursing practice in Saudi Arabia by obtaining expert consensus and to recommend a future agenda for policymakers and researchers in the field of mental health nursing | A Delphi method was used. The data was collected over three rounds. For the first round, the researcher utilized open-ended question questionnaire. Following the content analysis of the open-ended questions (639) responses was elicited. A 33 items questionnaire was then constructed with five major categories and was utilized later during the second and third round of the study. | The first consist of faculty members from eight Saudi universities and the second consist of nursing staff from three major Saudi mental health hospitals. The questionnaires were sent by email to the faculties and directly to the nursing staff | In KSA | The results of the study showed that consensus among the experts were reached on 19 elements with agreement level of 80% or more. In conclusion, it was apparent that expert panel believes that there are many elements that should shape up the future of mental health nursing practice by 2025. However, less emphasis was apparent from the panel ratings on items such as the stigma associated with mental illness and mentally ill people |
| Alyousef et al. [28] | This study aims to characterize the ideas that advanced mental health nurse practitioners hold about supervision in practice and to consider what is required to support changes to advanced mental health nursing in Saudi Arabia | This study adopted a qualitative exploratory design that applied a phenomenological approach as the research method. | Twelve postgraduate mental health nurses were recruited through purposive sampling | In Saudi Arabia | The data analysis generated the central theme, which indicates the attributes of a competent supervisor of advanced mental health nurse practitioners. The components of a supervisor’s competence had the following three main themes: nursing competencies, professional characteristics and communication |
| Alhamidi et al. [29] | The aim of this study is to investigate the roles of psychiatric mental health nurses during their work experiences in inpatient clinical settings | A focus group study | 10 graduate psychiatric nurses with more than 2 years’ practice in inpatient psychiatric settings | In KSA | Multiple practice issues emerged. The participants perceived that psychiatric nurse specialists are required to perform more caring functions than practicable in the inpatient setting due to an excess of no caring duties, structural minimization of the caring role and inadequate training. They felt that many of the functions performed were not within their expectations of the caring role of a psychiatric nurse specialist and believed that changes in nurse education and attention to clarification of nurse’s roles might enhance the role they play in patient care |
Quality assessment
The included studies methodological quality and bias risk were evaluated using relevant quality assessment tools adapted to various study designs. This process ensured that the research was a compact and trustworthy source of knowledge as shown in Table 5 [22-30]. The sub-themes observed among the studies, including in the systematic review was shown in Table 6.
| S. no. | Author | Are the selection of studies described appropriately | Is the literature covered all relevant studies | Does the method section describe? | Were findings clearly described? | Quality rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alzahrani et al. [22] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 2 | Aljohani et al. [23] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 3 | Alyousef et al. [24] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 4 | Alzghool et al. [25] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 5 | Alhawsawi et al. [26] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 6 | Aldhafeeri et al. [27] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 7 | Aljohani et al. [23] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 8 | Alyousef et al. [28] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 9 | Alhamidi et al. [29] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
| 10 | AlOtaibi et al. [30] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Good |
Note: The systematic review of studies provided clear descriptions, methods, selection processes, literature coverage and clear conclusions, resulting in a "Good" rating for their quality.
| S. no. | Themes |
|---|---|
| 1 | Educational interventions increase the practice of psychiatric nursing |
| 2 | Mental health challenges impact psychiatric nurse’s practices |
| 3 | Institutional policy impact on psychiatric nurse’s practices |
| 4 | Mental health regulation and stigmatization |
| 5 | Developing professional attitude toward psychiatric disorder |
| 6 | Defined psychiatric nurse’s roles within the psychiatric setting enhance psychiatric practice |
Discussion
The three main themes and nine subthemes in the literature review were knowledge of consumer’s recovery, educational resources, and nurses' learning experiences. Using a multidisciplinary approach and performance indicators, as well as involving customers, was the initial subject. Learning and planning care with a recovery-focused system were the focal points of the second topic. Under the third theme, recovery was examined, along with the benefits of recovery-oriented activities and educational initiatives [31].
The study shows that stigmatizing perceptions regarding mental illness and mental health nursing are common among nursing students in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Various factors influence these views, including professional experience, personal experience and cultural standards. Educational strategies that combat these stigmas include direct interaction, films and lectures. More research is necessary to understand the causes of these misconceptions and determine the best courses of action for lowering stigma among Saudi Arabian nursing students [32]. The analysis found several anti-stigma programs that improved the perceptions of mental illness among mental health practitioners. The effectiveness of contact-based therapies was discovered. However, educational plans for particular mental diseases were proposed to psychiatric nurses [33].
Moreover, students said the doctor’s round was significant because of its open environment, knowledgeable staff and well-defined procedures. However, the students felt uneasy because of the unclear directions and their little knowledge of psychiatric care. Although it takes careful planning and preparation, the school is an excellent example of how interprofessional competencies may be incorporated into ward visits [34].
The institutional policy is also crucial in psychiatric settings for psychiatric nursing staff. The research concluded that inter-institutional collaborations could transform primary healthcare and promote dialogue about nursing. Important stakeholders must show they are willing to contribute time and money by being actively involved. Leadership and a clear strategic direction are also essential. Leaders in executive management ought to be educated and developed [35].
The study discovered that although participant’s knowledge and attitudes toward some aspects of mental illness were favourable, their attitudes towards other parts of the condition were negative. Most participants felt that patients should be treated respectfully and that medicine effectively treats mental illness. Nevertheless, 36% of participants thought that people with mental illness were usually aggressive and 33% thought that hospitalization would increase community safety. Additionally, the study discovered a robust inverse relationship between adult’s attitudes and their preparedness to engage with patients.
Moreover, nursing attitudes towards psychiatric disorders lead to their effective practice within the psychiatric ward. The study’s two primary themes-the occurrence of violence and its cause were found through data analysis using semi-structured interviews. Even though they saw it as a necessary part of their job, it was discovered that the violence of their female patients badly impacted female psychiatric nurses [18]. However, psychiatric nurses perform effectively if their roles are defined to them.
Psychiatric institutions regulate mental health services by providing education, awareness programs and training to psychiatric nurses [28].
Conclusion
It is concluded that defined roles, psychiatric institutions’ rules and regulations, and education and training provided to the psychiatric nurses have positively related to nurses practice within the psychiatric ward. Furthermore, the studies chosen had used well-established scales for measurement and provide valuable data on team dynamics. The data collected from Scopus, PubMed and Web of Science are effective and played an important role in the study. The more policies are defined for psychiatric nurses, the more effective service or treatment they will provide to the patients.
Limitations
The risk of publication bias limits this systematic review because only published studies were included. This may result in removing unreported or grey material lacking information concerning mental health policies and regulations affecting psychiatric nursing practice in Saudi Arabia. There were more quantitative or cross-sectional studies. Qualitative research needs to evaluate the nurses' perceptions and attitudes about mental health regulation and policies in a psychiatric setting.
Suggestions
Future studies could use unpublished information and research from government-run and non-profit groups and engage subject-matter experts to reduce this limitation. It is suggested to identify the mental health policy and regulation among all hospital settings in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA).
Recommendations
Exploring factors associated with the mental health policies and regulations affecting psychiatric nursing practice are recommended. Identifying the common themes among psychiatric nursing and psychiatrists is also recommended. Researchers, including nurses, should do future studies to determine more about regulating mental health services within the psychiatric hospital. It is also necessary for the psychiatric hospital to develop mental health policies for psychiatric nurses.
References
- Fusar-Poli, Paolo, Gonzalo Salazar de Pablo, Andrea de Micheli, and Dorien H Nieman, et al. "What is Good Mental Health? A Scoping Review." Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 31 (2020):33-46.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Batool, Rubia, Amna Khan, Sayed Shahbal, and Ali Ibrahim Noshili, et al. "Relationship among Locus of Control, Personality Type and Subjective Happiness among Conversion Patients and Healthy Individuals." Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses 16 (2022):1-5.
- Liese, Bernhard H, Rebecca SF Gribble, and Marisha N Wickremsinhe. "International Funding for Mental Health: A Review of the Last Decade." Int Health 11 (2019):361-369.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- World Health Organization. Comprehensive Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2030. (2021).
- Noshili, Ali Ibrahim, Rubia Batool, Ahmed Abdu Najmi, and Majed Abdullah Najmi, et al. "Relationship between Personality Trait and Mental Health Well-Being, the Mediating Role of Emotional Intelligence among Healthcare Workers in Jizan, KSA." J Posit Sch Psychol 6 (2022):1833-1851.
- Wadoo, Ovais, Shiekha Haya Abdulla QF Althani, Javed Latoo, and Majid Alabdulla. "Policy and Legislation for the Treatment of Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders in Qatar." Asian J Psychiatr 79 (2023):103368.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Akther, Syeda Ferhana, Emma Molyneaux, Ruth Stuart, and Sonia Johnson, et al. "Patient’s Experiences of Assessment and Detention under Mental Health Legislation: Systematic Review and Qualitative Meta-Synthesis." BJPsych Open 5 (2019):e37.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Hussain, Shakir, Ali Ibrahim Noshili, Sayed Shahbal, and Amal Mohammad Hamdi, et al. "A Comparative Account on Ethical Considerations in Practice of Clinical Psychology." Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses 16 (2022):1-4.
- Shubayra, Amnah A, Fatima S Alhwsawi, Feryal F Alsharar, and Sayed Shahbal. "Relationship between Nurses' Satisfaction and their Perception of Nepotism Practice in Workplace." J Jilin Univ 41 (2022):138-160.
- Almutairi, Abdulhamid Mulfi, Sayed Shahbal, Saeed Mohammed Alzahrani, and Rawan Abdulrahman Aladah, et al. "Association between Locus of Control of Health, Religious Attitude, and Spirituality in Older Adults in Psychiatric Hospitals of Jeddah." J Posit Psychol Wellbeing (2022):161-171.
- Moreno, Carmen, Til Wykes, Silvana Galderisi, and Merete Nordentoft, et al. "How Mental Health Care Should Change as a Consequence of the COVID-19 Pandemic." Lancet Psychiatry 7 (2020):813-824.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Havaei, Farinaz, Andy Ma, Sabina Staempfli, and Maura MacPhee. "Nurses’ Workplace Conditions Impacting their Mental Health during COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study." Healthcare 9 (2021):84.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Ricci-Cabello, Ignacio, Jose F Meneses-Echavez, Maria Jesús Serrano-Ripoll, and David Fraile-Navarro, et al. "Impact of Viral Epidemic Outbreaks on Mental Health of Healthcare Workers: A Rapid Systematic Review." MedRxiv (2020):1-91.
- Alqarni, Mariyam Aied, Hamdan Saud Alotaibi, Hussam Madani Samaren, and Adil Aid Alharby, et al. "Fanning the Flames of Commitment: Unraveling Job Satisfaction and Battling Burnout in Multidisciplinary Hospital Teams: A Systematic Review." J Namibian Stud 35 (2023):172-198.
- Alotaibi, Azah Bajad, Sayed Shahbal, Fatimah Abdullah Almutawa, and Hussain Salem Alomari, et al. "Professional Exhaustion Prevalence and Associated Factors in Doctors and Nurses in Cluster One of Riyadh." J Posit Sch Psychol (2022):94-109.
- Shahbal, Sayed, Amna Khan, Ayat Mohamed Ahmed Zammar, and Amal Mohammad Hamdi, et al. "Technology Addiction, Sleep Disturbance and Physical Inactivity among Psychiatric Patients." Int J Clin Skill 16 (2016):231.
- Shahbal, Sayed, Ali Ibrahim Noshili, Amal Mohammad Hamdi, and Ayat Mohamed Ahmed Zammar, et al. "Nursing Profession in the Light of Social Perception in the Middle East." J Posit Psychol Wellbeing 6 (2022):3970-3976.
- Alanazi, Badriah, Sue McAndrew, and Tony Warne. "Female Patient Violence Experienced by Female Qualified Nurses Working in an Inpatient Psychiatric Department." Int J Ment Health Nurs 32 (2023):1315-1325.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Ventura, Carla Aparecida Arena, Wendy Austin, Bruna Sordi Carrara, and Emanuele Seicenti de Brito. "Nursing Care in Mental Health: Human Rights and Ethical Issues." Nurs Ethics 28 (2021):463-480.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Alruwaili, Samiyah Obaylik Muqanna, Sayed Shahbal, Farah Awadh Alharbi, and Wafa Ahmed Makrami, et al. "The Effect of Workload on the Commitment to Work for the Nurses, A Systematic Review." J Posit Sch Psychol 6 (2022):2880-2896.
- Sindhu, Zeeshan Mehfooz, Sayed Shahbal, Samreen Khurshid, and Nasra Irshad, et al. "Death Anxiety and Life Satisfaction among Health Workers during COVID-19; with Moderating Role of Optimism." J Xi’an Shiyou Univ 18 (2022):199-220.
- Alzahrani, Manal SJ and Loujain S Sharif. "Effectiveness of an Educational Intervention on Clinical Competency among Mental Health Nurses Working at a Government Mental Health Hospital: A Quasi-Experimental Study." Open Nurs J 17 (2023):1-8.
- Aljohani, Khaleel Ibraheem, Muneeb M Alzghool, and Abdulrhman Mohammad Albakiri. "Community Mental Health Nursing in Saudi Arabia: Current and Future Challenges." Eur Online J Nat Soc Sci 10 (2021):592.
- Alyousef, Seham Mansour, and Sami Abdulrahman Alhamidi. "Nurse Views of Obstacles Encountered by Nurses in Saudi Arabia during the Provision of Psychiatric Care." Arch Psychiatr Nurs 44 (2023):8-17.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Alzghool, MM, and AM Al-Bakiri. "The Future of Mental Health Nursing Practice in Saudi Arabia: A Delphi Study." J Comp Nurs Res Care 4 (2019):132.
- Alhawsawi, Afrah Mousa, Khalid Matar Alsohimi, Misfer Saeed Awadie, and Bandar Awadh Alshehri. "Nurses’ Attitude towards Patient’s Rights at Erada Mental Health Complex in Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia." Emerg Med Sci (2022):47-54.
- Aldhafeeri, Eisa Turqi Ghanem, Saadoun Tarqi Ghanem Aldhafeeri, Hani Tarqi Ghanem Aldhafeeri, and Mutar Awaid Asaim Aldhafeeri, et al. "Difficulties Experienced by Psychiatric Nursing in Mental Health Hospitals and Clinics and their Relationship to Performance Improvement." Saudi J Nurs Health Care 5 (2022):261-272.
- Alyousef, Seham Mansour, and Sami Abdullrahman Alhamidi. "Evaluating the Need for Supervision of Advanced Mental Health Practitioners in Psychiatric Practices in Saudi Arabia." Ment Health Soc Incl (2022).
- Alhamidi, Sami Abdulrahman, and Seham Mansour Alyousef. "Perceptions of Saudi Psychiatric Mental Health Nurses Roles in the Inpatient Mental Health Care Setting." Arab Gulf J Sci Res (2023):1-15.
- AlOtaibi, Nora Ghalib, Amira Alshowkan, Neama Kamel, and Ayman Mohamed El-Ashry, et al. "Assessing Perceptions about Critical Thinking, Motivation Learning Strategies in Online Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing Education among Egyptian and Saudi Undergraduate Nursing Students." BMC Nurs 22 (2023):1-13.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Hawsawi, Tahani, Jane Stein‐Parbury, Fiona Orr, and Michael Roche. "Exploring Recovery‐Focused Educational Programmes for Advancing Mental Health Nursing: An Integrative Systematic Literature Review." Int J Ment Health Nurs 30 (2021):1310-1341.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Alharbi, Raghad B. "The Prevalence of Stigmatizing Beliefs towards Mental Illness and Mental Health Nursing among Third-Year Undergraduate Nursing Students in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A Review." Eur J Med Health Sci 5 (2023):41-48.
- Sukut, Ozge, Gizem Sahin‐Bayindir, C Hurrem Ayhan‐Balik, and Esra Albal. "Professional Quality of Life and Psychological Resilience among Psychiatric Nurses." Perspect Psychiatr Care 58 (2022):330-338.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Aditya, Ronal Surya, Lailatul Kodriyah, Ah Yusuf, and Fitriana Kurniasari Solikhah, et al. "Analysis of Organizational Culture Factors that Influence the Performance of Health Care Professionals: A Literature Review." J Public Health Afr 13 (2022):1-5.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Albalawi, Amal HS, Fathia K Kassem, and Nofaa A Alasmee. "Nurse’s Perception toward Factors Contributing to Violence Exposure at Complex for Mental Health in Tabuk City: A Scoping Review." Evid Based Nurs Res 4 (2022):1-17.
Citation: Alanazi, Wael Habib, Abdulrahman Nayir Alanazi, Faisal Najem Khalaf Aljohani and Sehrish Khan, et al. “Mental Health Policies and Regulations Impacting Psychiatric Nursing Practice in Saudi Arabia.” Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses 17 (2023). DOI: 10.3371/CSRP.AWAA.100623
Copyright: © 2023 Alanazi WH, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.