Short Communication - Clinical Schizophrenia & Related Psychoses ( 2021) Volume 0, Issue 0
Serotype and Virulence Gene of E.coli and Associated with Rota Virus Isolated from Patients with Diarrhea Infection
Zahrah Adnan Al-Shammarri*Zahrah Adnan Al-Shammarri, Department of Science, University of Misan, Amarah, Iraq, Email: russia_201369@yahoo.com
Received: 19-Jul-2021 Accepted Date: Aug 02, 2021 ; Published: 09-Aug-2021
Abstract
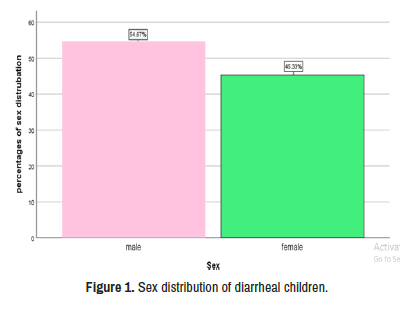
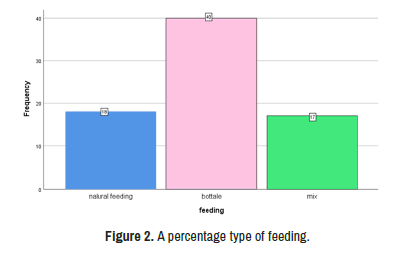
Diarrheal infection are a sever public health problem and a major causes of mortality of children . E.coli is one the most important microbial agent of diarrhea. Rotavirus is the most common causes of sever gastroenteritis and diarrhea in infant and young children in world. Seventy-five diarrheal samples was isolated from children have sign and symptoms as diarrhea, vomiting abdominal pain and dehydration. Samples were isolated from Al- sadder hospital/pediatric department from January to May 2020. In material and methods was been used bacteriological culture media, biochemical test, Gram stain and Vitek-2 to detect E.coli in 37C° for 24 hr . For detection of Rota virus use Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Cav C gene and Tra t gene are a virulence factors gene in E.coli were detected by DNA extraction and Conventional PCR .In the results age groups and sex distribution with diarrheal infection male was 41 (54.7%) and female 34 (45.3%) regarding to sex distribution with E.coli and Rota virus male is more effective with E.coli 17 (41.5%) and female 20 (58.8%) but Rota virus associated with diarrheal and male was recorded 12 (29.3%) and female (11.82%). E.coli was enrolled 37 (49.34%), Rota virus 23 (30.7%) and mix infection 16 (20%) Based on types of feeding bottle feeding was recorded a high rate (40%) which causes diseases. A virulence (gene tra T and cva C) gene in E.coli was detected.
Keywords
Serotype of E.coli • E.coli • Rotavirus • Virulence genes
Description
Diarrheal infection that causes death in age groups in children between (1-5) years old. About 760,000 of children which was dead every year [1]. Some microorganism that causes diarrhea in the world as Escherichia coli Enterhemorrhagic E.coli and Rota virus [2]. Escherichia coli is a normal flora of human in large in human and warm blooded animals, some strain are pathogenic and some strain of E.coli transfer plasmid DNA responsible for enterotoxin or invasive factors. E.coli is responsible about neonatal diarrheal infection, neonate meningitis bacteremia hemolytic uremic syndrome [3]. Escherichia coli is a bacillus or red, gram negative related to Enterobacteriaceae family, facultative anaerobic and spore forming. E.coli has capsular Antigen (K-Antigen) or Somatic Antigen (O-Antigen), these causes (40%) of cases septicemia and (80%) of cases meningitis (3). Diarrheal diseases are one of sever health problem and a major causes of morbidity and mortality in infants and younger children [4]. E.coli has outer membrane of Lipid Polysaacride (LPS) this structure referred to O-Ag [5]. The conventional serotypes methods are based on agglutination reaction of O-Ag with antisera that are generated in rabbit against O-antigens 5. Rotavirus infections are a major cause of diarrhea in children and domestic animals, and age of children range between 5 years of life [6]. In the third world and developing countries Rota viral gastrointestinal disease, the development of potential inhibitors of this virus is of great interest [7].
Rotavirus, an icosahedral virus related to family Reoviridae. Bishop was first recognized as a diarrhea infection [8]. Rotavirus particle consists of three protein layers was called triple-layered particle diagnosis by electron-microscopy, it was look like wheels (Latin Rota), and give name Rotavirus for the genus [9]. Rotavirus was the most common cause of severe childhood diarrhea in worldwide which causes diarrheal mortality in developing countries [10]. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that (527,000) children under the age (5) years die of rotavirus disease each year. Currently available rotavirus vaccines protected against severe Rotavirus gastroenteritis and were well tolerated the implementation of immunization programs would be expected to reduce disease burden. Most local previous studies detect the most common cause diarrhea in children as virus infection or bacterial infection in separate studies [11]. A virulence determinant acquired, virulence mechanisms, host colonization and clinical manifestation these factors used for classified pathotypes in to Enteropathogenic E.coli (EPEC), Enterohemorrhagic E.coli (EHEC), Enteraggregation E.coli (EAEC), Enterotoxgenic E.coli and Enteroinvasive E.coli [12].
Identification and isolation
A total of (75) of diarrheal stool was taken from children with age groups range from (1-24) months were culture on Macconcy, Blood, and Eosin methylene blue agar. E.coli colonies were diagnosis by Gram stain, biochemical tests and Vitek-2 [13].
DNA extraction and protocol of amplification of virulence genes
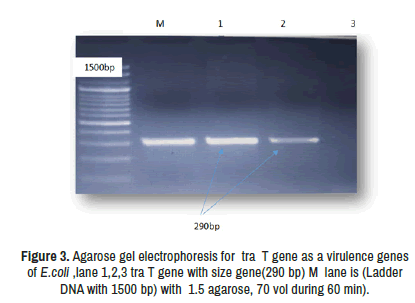
For amplification condition of virulence, genes depend on Yamamoto et al., [14] Table 1.
| Name |  |
Size gene ref |
|---|---|---|
| Tra T | F-GGTGTGGTGCGATGAGCACAG R-CACGGTTCAGCCATCCCTGAG |
290 bp [15] |
| Cva C | F- CACACACAAACGGGAGCTGTT R’- CTTCCCGCAGCATAGTTCCAT |
680 bp [15] |
Table 1: Oligonucleotide primers for virulence factors genes. Identification of serotypes of E.coli.
All strain of E.coli were serotyped depend on O-Antigen and H-Antigen of agglutination methods was used according to [16].
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
All diarrheal samples were detected for Rota virus by ELISA kite (RIDASREEN® Germany kite) by monoclonal antibodies are used in a sandwich type method in micro well plate [17]. In accurate results was been showed E.coli is more effective is more effective from Rotavirus to causes diarrheal in children, which have sign and symptoms as diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting and dehydration .According to age groups of children which was sever from diarrhea infection was range from (1-24) month. All children who has clinical manifestation as diarrheal, high fever, abdominal pain, vomiting and dehydration. In Table 2 age groups associated with sex distribution.
| Age groups (months) | Frequency % |
Male | Female | Total | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-4 | 8 (10.3) | 5 (31.3) | 3 (37.5) | 8 (100) | 0.35* |
| 5-9 | 21 (26.9) | 9 (45) | 11 (55) | 20 (100) | |
| 10-14 | 21 (26.9) | 1(61.9)3 | 8 (38.1) | 21 (100) | |
| 15-19 | 16 (20.5) | 1(68.9)1 | 5 (31.3) | 16 (100) | |
| 20-24 | 9 (11.5) | 3 (33.3) | 6 (66.7) | 9 (100) | |
| Total | 78 (100) | 4(54.7)1 | 3(45.3)4 | 75 (100) |
Table 2: Age groups and sex distribution of diarrheal children.
The high percentage was enrolled in age groups (5-9) month was in male is lower 9(45%) than female 11(55%) also age group (10-14) month as in male was a high percentage 13 (61.9%) than female 8 (38.1%) then related to natural of breast feeding natural or bottle feeding, genetic and nutritional factors and other Socioeconomic factors such as mothers education, residences and sample size for study. Some local study in Iraq were enrolled as the following studies in Basra (24%) in 2003, Erbile (37%) in 2006 also in 2011 study was recorded (30%) of diarrhea infection and finally in Ramadi and Hella were (39.26%) and (52.54%) respectively FR [18-20] E.coli was recorded 37(100%) in both sex and high rate in female 20(58.8%) and Rota virus was reported a lower rate 23(111.7%) and more rate in male 12(29.3%) as in Table 3. Abdollah , et al., was recorded a high rate in female 25(0.30%) these disagrees with this study was (54.67%) in male a high rate and low rate in female (45.33%) [21] (Tables 4-6) (Figures 1-4).
| Sex distribution | E.coli | Rota virus | Mix infection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 17 (41.5) | 12 (29.3) | 12 (29.3) |
| Female | 20 (58.8) | 11 (82.4) | 3 (8.8) |
| Total | 37 (100) | 23 (111.7) | 15 (38.1) |
Table 3:Sex distribution associated with E.coli and Rota virus.
| Age group (month) | E.coli | Rota virus | Mix infection | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-4 | 5 (62.5) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (25) | 8 (100) |
| 5-9 | 12 (60) | 4 (19) | 5 (23.8) | 21 (100) |
| 10-14 | 8 (38.1) | 10 (47.6) | 3 (14.3) | 21 (100) |
| 15-19 | 8 (38.1) | 5 (31.3) | 3 (18.8) | 15 (100) |
| 20-24 | 14 (44.4) | 3 (33.3) | 2 (22.2) | 9 (100) |
| Total | 37 (49.3) | 23 (30.7) | 16 (20) | 75 (100) |
Table 4: Age groups associated with E.coli and rota virus.
| E.coli serotypes | Positive cases | % |
|---|---|---|
| O194:H23 | 4 | 26.66 |
| O128:H2 | 3 | 20 |
| O142:H6 | 3 | 20 |
| O128:H7 | 2 | 13.33 |
| O148:H28 | 2 | 13.33 |
| O7:H152 | 1 | 6.66 |
| Total | 15 | (100%) |
Table 5: Serotype of E.coli associated with diarrhea.
| Type of feeding | E.coli % | Rota virus % |
Mix infection % |
P-vale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast feeding | 10 (27) | 0 | 8 (53.3) | 0.001* |
| Bottle feeding | 19 (51.4) | 14 (60.9) | 7 (46.7) | |
| Mix infection | 8 (21.6) | 9 (39.1) | 0 | |
| Total | 37 (100%) | 23 (100%) | 15 (100%) |
Table 6: Type of feeding associated with diarrheal agent (P 0.05). *
References
- World Health Organization [WHO]. Fact Sheet N 330. Geneva, Switzerland. (2013).
- Parashar, Umesh D, Bresee Joseph S, Gentsch JR and Glass RI. “Rotavirus.” Emerg Infect Dis 4 (1998): 561-570.
- Bhavsar, Sejal Makvana and Krilov Leonard R. “Escherichia coli Infections.” Pediatrics in Review 36 (2015): 167-171.
- World Health Organization [WHO]. World Health Statistics. Geneva, Switzerland. (2012).
- Sarkar, Sohinee, Ulett Glen C, Totsika Makrina and Phan Minh-Duy, et al. “Role of Capsule and O Antigen in the Virulence of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.” PLoS One 9 (2014): e94786.
- ørskov, I, ørskov F, Bettelheim KA and Chandler ME. “Two New Escherichia coli o Antigens, O162 and O163, and One New h Antigen, H56. Withdrawal of h Antigen H50.” Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B 83 (1975): 121-124.
- Bishop, RF, Davidson GP, Holmes IH and Ruck BJ. “Virus Particles in Epithelial Cells of Duodenal Mucosa from Children with Acute Non-Bacterial Gastroenteritis.” Lancet 2 (1973): 1281-1283.
- Desselberger, Ulrich. “Rotaviruses.” Virus Research 190 (2014): 75-96.
- Widdowson, Marc-Alain, Steele Duncan, Vojdani Jazmin and Wecker John, et al. “Global Rotavirus Surveillance: Determining the Need and Measuring the Impact of Rotavirus Vaccines.” J Infect Dis 200 (2009): S1-S8.
- Grimwood, Keith and Lambert Stephen B. “Rotavirus Vaccines: Opportunities and Challenges.” Hum Vaccin 5 (2009): 57-69.
- Croxen, Matthew A, Law Robyn J, Scholz Roland and Keeney Kristie M, et al. “Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli.” Clin Microbiol Rev 26 (2013): 822-880.
- Forbes, Betty, Sahm Daniel, and Weissfeld Alice. “Study Guide for Bailey and Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology 12th Edition.” Mosby (2007).
- Yamamoto, Shingo, Nakano Masayuki, Terai Akito and Yuri Kazuyo, et al. “The Presence of The Virulence Island Containing the usp Gene in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli is Associated with Urinary Tract Infection in An Experimental Mouse Model.” J Urol 165 (2001): 1347-1351.
- Johnson, JR, and Stell AL. “Extended Virulence Genotypes of Escherichia coli Strains from Patients with Urosepsis in Relation to Phylogeny and Host Compromise.” J Infect Dis 181 (2000):261-272.
- Edwards, Philip R and Ewing William H. “Edwards and Ewing's Identification of Enterobacteriaceae 4th Edition.” : Elsevier (1986).
- Al-Shuwaikh, Arwa Mujahid Abdullah, Ibrahim Israa Aj and Abdullah Rana Mujahid. “Detection of E. coli and Rotavirus in Diarrhea among Children Under Five Years Old.” Iraqi Journal of Biotechnology 14 (2015): 85-92.
- Mahmood, Dhia A. and Feachemt Richard G. “Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Rotavirus- and EPEC-Associated Hospitalized Infantile Diarrhoea in Basrah, Iraq.” J Trop Pediatr 33 (1987): 319-325.
- Ahmed, Herish M, Coulter J Brian S, Nakagomi Osamu and Hart CA, et al. “Molecular Characterization of Rotavirus Gastroenteritis Strains, Iraqi Kurdistan.” Emerg Infect Dis 2 (2006): 824-826.
- Abdulrazzaq, A, Aljeboory SK, Abdul Kareem S and Klena J. Two Different Diagnostic Methods for Detection of Rotavirus in Iraqi Young Children. Al-Anbar J Vet Sci 4 (2011): 52.
- Naficy, AB, Abu-Elyazeed R, Holmes JL and Rao MR, et al. “Epidemiology of Rotavirus Diarrhea in Egyptian Children and Implications for Disease Control.” Am J Epidemiol 150 (1999): 770-777.
- Yang, CC and Konisky J. “Colicin V-treated Escherichia coli Does not Generate Membrane Potential.” J Bacteriol 158 (1984): 757-759.
Citation: Al-Shammarri, Zahrah Adnan . " Serotype and Viru-lence Gene of E.coli a nd Associated with Rota Virus Isolated from Patients with Diarrhea Infection”. Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses 15S(2021). Doi: 10.3371/CSRP. AZ.3010:52.
Copyright: © 2021 Al-Shammarri ZA. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.